Biogas
Development of Biomethanation Technology for Utilization of Unused CO₂ in Biogas
Overview
Biomethanation is the technology of producing methane from carbon dioxide and hydrogen through the action of microorganisms.
Osaka Gas is working on technology development to produce e-methane from carbon dioxide in biogas produced by methane fermentation and green hydrogen.1
1. Hydrogen produced without emitting CO2 in the production process, typically using renewable energy
Background
In recent years, methane fermentation has been attracting attention as a carbon-neutral energy source because it allows recovery in the form of biogas from waste, containing 60% methane and 40% carbon dioxide.
While methane in biogas can be used to produce thermal energy, carbon dioxide accounting for 40% cannot be used as it is. Osaka Gas focused on biomethanation as a way to utilize this unused carbon dioxide.

Biomethanation Programs of Osaka Gas
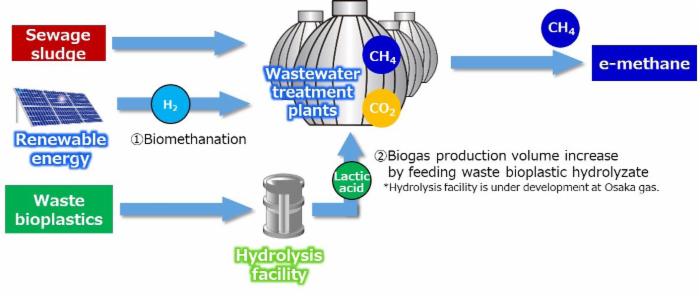
Since November 2022, Osaka Gas has been conducting a field test on biomethanation using biogas generated at a sewage treatment plant, jointly with Kyoto University, NJS Co., Ltd., and the municipal government of Osaka.
This field test uses a small-scale test facility newly constructed at the Ebie Sewage Treatment Plant in Osaka.The following two technological developments are being conducted.
- Sewage sludge and hydrogen are fed into the test facility, biogas is produced from the sewage sludge under the same conditions as those of the sewage treatment plant, and biomethanation3 is performed to synthesize e-methane from CO2 contained in the biogas and hydrogen, using microorganisms.
- A verification is conducted to increase the volume of biogas generated by feeding lactic acid, waste bioplastic hydrolyzate (WBH), into the test facility.
Achivements to date and future development
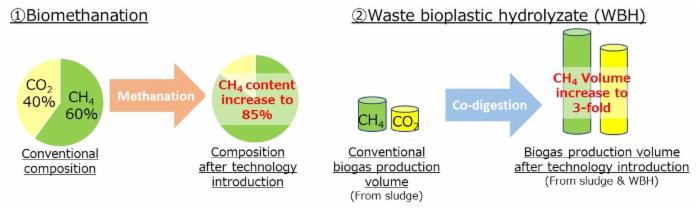
With biomethanation technology, the original methane content, approximately 60%, was increased to 85%, indicating that CO2 in biogas could be converted to energy. We are going to make futher improvement of methan content.
Regarding the technology for increasing biogas volume by feeding WBH, we have confirmed that stable operation can be conducted even when the biogas production volume is increased 3-fold, assuming a sufficient amount of WBH are prepared. We plan to scale up the experiment in the future, aiming of commercialization.
We will continue to develop these two technologies to introduce them on a full scale in the future.
Related contents
TAG SEARCH
- Evolving residential gas appliances
- Evolving residential gas appliances Water heaters, space heaters, dryers Cooking appliances Smart Equipment Fuel Cell systems
- Evolving commercial and industrial gas appliances
- Evolving commercial and industrial gas appliances Cogeneration (CHP) units Air conditioning systems, kitchen appliances Bio, water treatment Industrial furnaces, burners Energy management, IoT
- Enhancing the safety and economic efficiency of LNG regasification
- Enhancing the safety and economic efficiency of LNG regasification Utilization of cold energy Plant materials Power generation technology
- Developing next-generation businesses through enterprising initiatives
- Developing next-generation businesses through enterprising initiatives Materials development Measurement Simulation, data analysis Food science Material evaluation
- Contributing to conserving the environment and achieving a carbon neutral society
- Contributing to conserving the environment and achieving a carbon neutral society Methanation Hydrogen, ammonia Biogas Energy management Renewable Energy
- Technologies of Group companies
- KRI, Inc. Osaka Gas Chemicals Group OGIS-RI Group


