Materials development
Eco-friendly Biomass Material (Fluorene Cellulose)
Overview
Osaka Gas provides its original cellulose fiber (fluorene cellulose) that suppresses post-drying aggregation and exhibits high dispersibility in resins and organic solvents.
Background
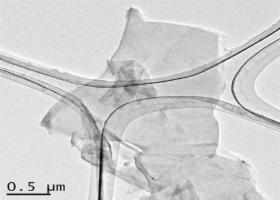
Cellulose fibers have one fifth the weight and five or more times the strength of steel, and one-fiftieth the thermal expansion coefficient of glass. They are promising as a plastic filler material alternative to glass fibers.
Cellulose fibers, however, have high hydrophilicity (high affinity for water), so that water loses its fluidity only with a several percentage addition of them in water. Furthermore, cellulose fibers dispersed in water will aggregate when dried, which makes it difficult to mix with commodity plastics, making them difficult to use.
The Daigas Group modified the cellulose fiber surface by its original fluorene material to develop fluorene cellulose that is inhibited from aggregation when dried.

Action
Fluorene cellulose, which contains little water, can be provided as a dry powder. Dispersed in alcohol, ether, or other organic solvents, it becomes suitable for coating applications. Moreover, for resin compounds, it can be provided as a masterbatch, being dispersed in resins such as polyamide (PA), polyethylene (PE), and polylactide (PLA).
In particular, by mixing fluorene cellulose with a resin, it is possible to make the product lightweight, stronger, dimensionally stable, and recyclable. We are currently actively providing it in the form of a resin masterbatch as a sample and having it evaluated in various applications.
Related contents
TAG SEARCH
- Evolving residential gas appliances
- Evolving residential gas appliances Water heaters, space heaters, dryers Cooking appliances Smart Equipment Fuel Cell systems
- Evolving commercial and industrial gas appliances
- Evolving commercial and industrial gas appliances Cogeneration (CHP) units Air conditioning systems, kitchen appliances Bio, water treatment Industrial furnaces, burners Energy management, IoT
- Enhancing the safety and economic efficiency of LNG regasification
- Enhancing the safety and economic efficiency of LNG regasification Utilization of cold energy Plant materials Power generation technology
- Developing next-generation businesses through enterprising initiatives
- Developing next-generation businesses through enterprising initiatives Materials development Measurement Simulation, data analysis Food science Material evaluation
- Contributing to conserving the environment and achieving a carbon neutral society
- Contributing to conserving the environment and achieving a carbon neutral society Methanation Hydrogen, ammonia Biogas Energy management Renewable Energy
- Technologies of Group companies
- KRI, Inc. Osaka Gas Chemicals Group OGIS-RI Group